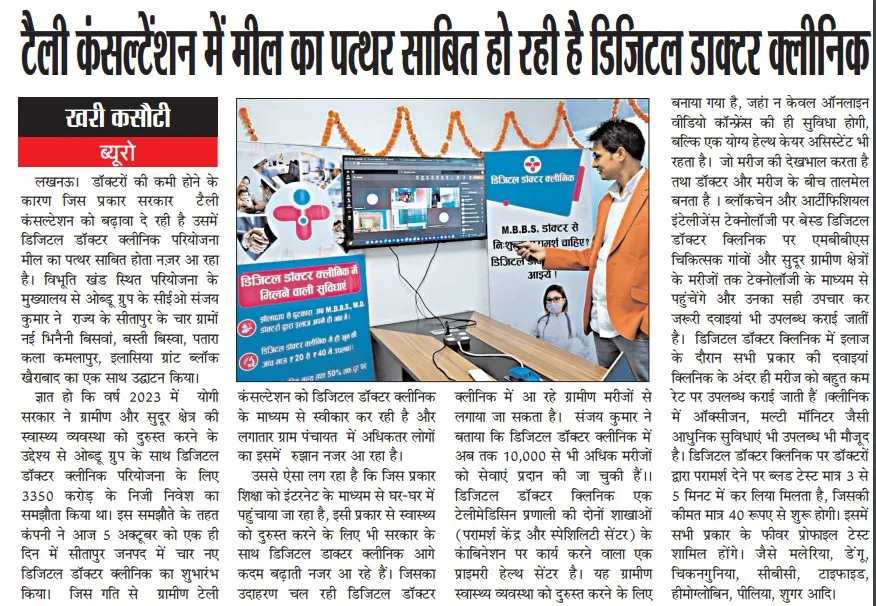
उत्तर प्रदेश सरकार की ओर से उत्तर प्रदेश के लिए। ओब्डू के साथ समझौता ज्ञापन 23/HEALTH/0000010982



Vitamin B12: An Essential Nutrient for Health
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a vital nutrient that plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health. It is involved in numerous bodily processes, including the formation of red blood cells, maintenance of a healthy nervous system, and DNA synthesis. A deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to a variety of health issues, ranging from mild to severe.
Functions of Vitamin B12
- Red Blood Cell FormationVitamin B12 is essential for the production of red blood cells. Without adequate B12, red blood cells become abnormally large and irregularly shaped. This can lead to megaloblastic anemia, a condition characterized by fatigue and weakness.
- Nervous System HealthVitamin B12 is crucial for the maintenance of a healthy nervous system. It helps produce myelin, a protective sheath that covers nerve fibers. Myelin enhances the transmission of nerve impulses and ensures proper nerve function. A deficiency in B12 can lead to neurological issues such as tingling in the hands and feet, confusion, memory loss, and cognitive decline.
- DNA SynthesisVitamin B12 is necessary for DNA synthesis, which is essential for the production and maintenance of genetic material in all cells. This process is particularly important during periods of rapid cell division and growth, such as during pregnancy and infancy
Symptoms of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
- Fatigue and Weakness: A lack of red blood cells reduces the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood, leading to fatigue and weakness.
- Pale or Yellowish Skin: Anemia caused by B12 deficiency can result in pale skin, and in severe cases, jaundice
- Shortness of Breath and DizzinessReduced oxygen levels in the blood can cause shortness of breath and dizziness.
- Tingling Sensations: Nerve damage from B12 deficiency can cause tingling and numbness in the hands and feet.
- Loss of Appetite and Weight Loss: Gastrointestinal symptoms such as loss of appetite, weight loss, and diarrhea can occur.
- Cognitive Impairments: Confusion, memory loss, depression, and cognitive decline are possible symptoms due to the impact on the nervous system.
The symptoms of a vitamin B12 deficiency can vary depending on the severity of the deficiency. Common symptoms include
Causes of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
- Dietary Insufficiency: since B12 is primarily found in animal products. Those who do not consume enough meat, dairy, eggs, or other animal-derived foods are at risk.
- Absorption Issues: Certain medical conditions can interfere with the body's ability to absorb vitamin B12 from food. Conditions such as Crohn's disease, celiac disease, and pernicious anemia (an autoimmune condition affecting stomach lining cells that produce intrinsic factor) can lead to B12 deficiency.
- Medications: Certain medications can also interfere with vitamin B12 absorption. For example, metformin, a drug commonly used to treat diabetes, and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), used to treat acid reflux, can reduce the absorption of B12
Functions of Vitamin B12
- Red Blood Cell Formation: Vitamin B12 is essential for the production of red blood cells. Without adequate B12, red blood cells become abnormally large and irregularly shaped. This can lead to megaloblastic anemia, a condition characterized by fatigue and weakness.
- Nervous System Health: Vitamin B12 is crucial for the maintenance of a healthy nervous system. It helps produce myelin, a protective sheath that covers nerve fibers. Myelin enhances the transmission of nerve impulses and ensures proper nerve function. A deficiency in B12 can lead to neurological issues such as tingling in the hands and feet, confusion, memory loss, and cognitive decline.
- DNA Synthesis: Vitamin B12 is necessary for DNA synthesis, which is essential for the production and maintenance of genetic material in all cells. This process is particularly important during periods of rapid cell division and growth, such as during pregnancy and infancy
Preventing Vitamin B12 Deficiency
-
Dietary Sources: One of the best ways to prevent vitamin B12 deficiency is to consume a balanced diet rich in B12-containing foods. Excellent sources of vitamin B12 include:
- • Beef, fish, and poultry
- • Eggs and dairy products such as milk, cheese, and yogurt
- • Fortified cereals and nutritional yeast
- • Some plant-based milks and meat substitutes fortified with B12
- Supplements: For individuals who cannot get enough vitamin B12 from their diet, supplements are an effective alternative. Vitamin B12 supplements come in various forms, including tablets, capsules, and injections. It's essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage and form.
Importance of Vitamin B12 for Specific Populations
- Vegans and Vegetarians: Vitamin B12 is especially important for vegans and vegetarians, as their diets may lack sufficient amounts of this nutrient. Fortified foods and B12 supplements are often necessary to meet their nutritional needs.
- Older Adults: As people age, their ability to absorb vitamin B12 decreases. This can be due to changes in stomach acid production or the presence of medical conditions that affect absorption. Older adults should monitor their B12 levels and consider supplements if necessary.
Health Benefits of Vitamin B12
- Neurological Health: Vitamin B12 is essential for proper neurological function and helps reduce the risk of certain neurological diseases, such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and dementia. It supports brain health and cognitive function, contributing to mental clarity and mood stability.
- Cardiovascular Health: Vitamin B12 helps to protect the heart and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases. It works with folate and vitamin B6 to regulate homocysteine levels in the blood. High levels of homocysteine are associated with an increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Energy and Metabolism: Vitamin B12 plays a key role in energy metabolism. It helps convert food into energy, supporting overall energy levels and reducing fatigue. This makes it vital for maintaining a healthy metabolism and supporting physical and mental performance.
- Reproductive Health: Vitamin B12 may help improve fertility in both men and women. It is involved in DNA synthesis and the production of healthy eggs and sperm, supporting reproductive health and successful conception.
Conclusion
Vitamin B12 is a crucial nutrient essential for overall health and well-being. It supports the formation of red blood cells, maintains a healthy nervous system, and is necessary for DNA synthesis. A deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to a range of health issues, including anemia, neurological problems, and cognitive decline. Ensuring an adequate intake of vitamin B12 through diet or supplements is vital, particularly for those at risk of deficiency, such as vegans, vegetarians, and older adults. If you suspect a vitamin B12 deficiency, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action to maintain optimal health.