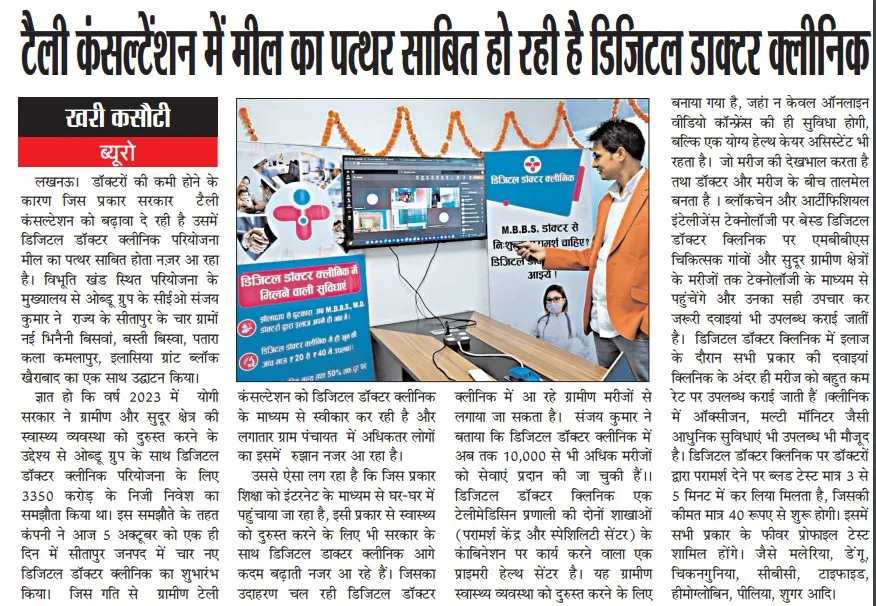
उत्तर प्रदेश सरकार की ओर से उत्तर प्रदेश के लिए। ओब्डू के साथ समझौता ज्ञापन 23/HEALTH/0000010982



Anxiety
Anxiety is a natural and common emotion that everyone experiences at various points in their lives. It is characterized by feelings of fear, worry, and unease about a specific event or situation. While anxiety can be a normal response to stress, it can become problematic when it is intense and persistent, significantly interfering with daily activities and overall well-being.
Understanding Anxiety
Anxiety manifests in a variety of ways, both physically and mentally. Physical symptoms of anxiety can include a racing heart, sweaty palms, trembling, muscle tension, restlessness, and fatigue. These physical responses are often due to the body's "fight or flight" response, which is triggered by perceived danger or threat.
Mentally, anxiety can lead to racing thoughts, persistent worry, difficulty concentrating, and an overwhelming sense of dread. Emotionally, individuals may experience feelings of apprehension, fear, and hopelessness. These symptoms can vary in severity and duration, but when they become chronic and interfere with daily life, they may indicate an anxiety disorder.
Types of Anxiety Disorders
- Anxiety disorders are the most common type of mental health disorder, affecting approximately 40 million adults in the United States alone. Some common anxiety disorders include:
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): Characterized by excessive, uncontrollable worry about various aspects of daily life. People with GAD often anticipate disaster and may be overly concerned about health, money, family, or work.
- Panic Disorder: Involves recurrent, unexpected panic attacks, which are sudden periods of intense fear that may include palpitations, sweating, shaking, shortness of breath, and a feeling of impending doom.
- Social Anxiety Disorder: Marked by an intense fear of social situations and being judged or scrutinized by others. This can lead to avoidance of social interactions and significant distress in social settings
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of anxiety disorders is not fully understood, but a combination of genetic, environmental, psychological, and developmental factors is believed to contribute. Risk factors for developing anxiety disorders include a family history of anxiety, traumatic experiences, chronic stress, and certain personality traits such as shyness or behavioral inhibition in childhood.
Treatment Options
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a widely used form of psychotherapy that has been shown to be particularly effective in treating anxiety disorders. It involves identifying and challenging negative thought patterns and behaviors and developing coping strategies to manage anxiety-provoking situations.
- Medications: Break your fitness goals into smaller, manageable milestones. Celebrating these achievements along the way will keep you motivated and focused.
- Antidepressants: Avoid monotony by mixing up your routine. Try different exercises, classes, or activities to keep things interesting and prevent boredom
- Anti-anxiety medications: Keeping a record of your progress can be a great motivator. Documenting your workouts and achievements helps you see how far you've come and encourages you to keep pushing forward
- Beta-blockers: These medications can help manage physical symptoms of anxiety, such as rapid heartbeat and trembling.
The good news is that anxiety is treatable. Effective treatments can help individuals manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. Two main types of treatment for anxiety disorders are psychotherapy and medication.
Seeking Help
It's essential to remember that everyone experiences anxiety differently, and there is no one-size-fits-all treatment. If you're struggling with anxiety, it's crucial to talk to a mental health professional who can help determine the best course of treatment for your specific situation. Early intervention can significantly improve outcomes and help you regain control over your life.